These new and improved features in Windows Server 8 will make many Windows administrators very happy.
Windows Server 8
The Windows 8 Consumer Preview--the desktop version of Windows 8--has been getting all of the attention lately, but another new kid is in town as well: Windows Server 8. Packing in tons of new features and improving many of the old ones, Microsoft has made Windows Server 8 a compelling platform for IT administrators.
Flexible Installation
Windows Server 8 should be easier to install than its predecessor, thanks to “scenario-based” deployment wizards that guide you as to which features and capabilities to enable depending on how the server will be used. It also provides admins the flexibility to switch between a core server install and a full Windows 8 GUI by adding or removing components after the fact.
ReFS (Resilient File System)
The new Resilient File System, or ReFS, replaces the venerable NTFS that most admins are familiar with. ReFS maintains backward compatibility with NTFS for features such as BitLocker data encryption and access control lists, but it includes a wide variety of new technologies designed to ensure that data integrity is maintained, and to prevent file corruption even in the event of a sudden loss of power.
Offloaded Data Transfer
If you are moving data from one SAN drive to another SAN drive across the network, you have no need to pass that data through the server. Windows Server 8 uses Offloaded Data Transfer to remove the server as the middleman, allowing the data to transfer with minimal impact to server resources or bandwidth.
Dynamic Access Control
Dynamic Access Control is a new file-authorization framework in Windows Server 8. Admins can define central, domain-level access policies that apply across the domain to all file servers. Dynamic Access Control policies are enforced in addition to the file and folder permissions that exist at the file level, and they override any conflicting permissions to ensure that data is protected.
DirectAccess
DirectAccess itself isn’t new. However, Microsoft has now combined DirectAccess and Routing and Remote Access Server (RRAS) into a unified tool that simplifies administration, configuration, and monitoring of remote devices. DirectAccess in Windows Server 8 is also capable of running over both IPv6 and IPv4 networks.
Server Management
Like so many other aspects of the Windows OS, management tools in Windows Server 8 sport a Metro UI face-lift. Admins will appreciate being able to add tiles for any of the physical or virtual servers on their network, as well as to easily view the current state and relevant details of all servers from one place. You can create a personalized dashboard displaying the server data most important to you, and manage servers simply by right-clicking the tiles.
IP Address Manager
Windows Server 8's new IP Address Manager tool greatly simplifies the job of keeping track of all those IP addresses. Admins can manage IP addresses, track IP address usage, and identify and resolve conflicts. The tool also provides an audit trail that can come in handy for tracing an IP address at a point in time for troubleshooting and incident response.
Hyper-V Clusters
Windows Server 8 supports clusters of insane proportions using Hyper-V. You can group up to 63 Hyper-V hosts, and as many as 4000 virtual machines in a single cluster. Windows Server 8 also includes various features to make managing and maintaining Hyper-V clusters easier, such as cluster-aware patching, data de-duplication, and BitLocker encryption for cluster volumes.
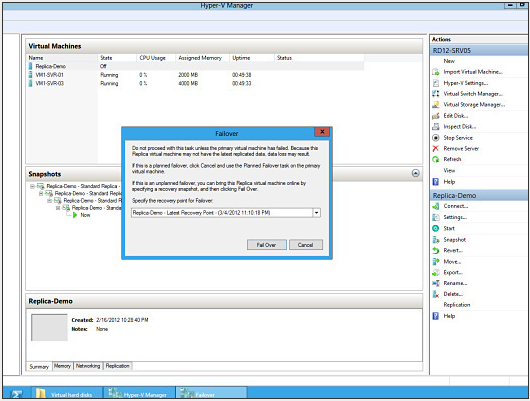
Disaster Recovery
You can use a Hyper-V Replica in Windows Server 8 as a standby server in the event of a server crash or other catastrophe. Windows Server 8 will continuously sync the original server with the Hyper-V Replica, so you always have a virtual server backup that is current within 5 minutes of the original, and can be configured for automatic failover and failback.
Simplified Live Migration
One of the biggest drawbacks of virtual machines in Hyper-V with previous versions of Windows was that migrating a virtual machine from one place to another was a clumsy process that could be both frustrating and time consuming. Windows Server 8 makes it much easier to migrate a running virtual machine in Hyper-V without interrupting productivity.
Thanks:NetworkWorld.com









No comments:
Post a Comment